Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
What is Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) and its advantages?
With natural intercourse, very few sperm cells are able to move through the cervical mucus that covers the cervix. Most of the sperm cells remain trapped in the vagina or the cervical mucus cover and never enter the uterus.
With intrauterine insemination (IUI), sperm can be drawn into a thin plastic catheter which is gently introduced through the cervix and placed at the top of the uterus where they can “swim” quickly to the fallopian tube.
With sperm washing, most of the healthy moving sperm can be concentrated to several drops which helps increase the number of sperm that are available for the fertilization of the egg during ovulation.
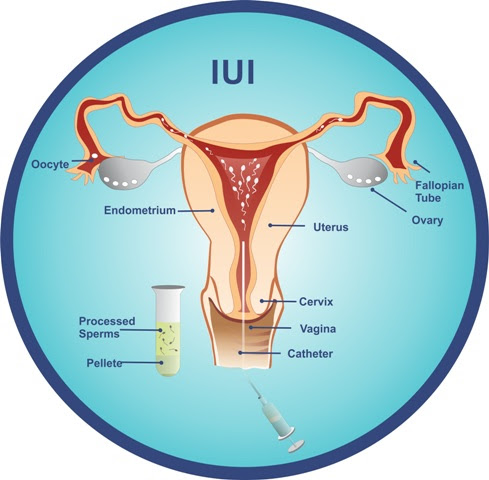
The most important advantage of IUI is it allows us to select out the healthy moving sperm and separate them from the non-moving sperms.
After the sperm cells have been selected, they are hyperactivated with a special fluid during sperm “washing” which allows them to move much quicker and greatly increase the likelihood of penetrating the barrier of the egg.
What patients benefit from IUI?
IUI is recognized by many fertility clinics as a first-choice option in cases of:
- male subfertility
- poor sperm quality – less than 4% of normal sperm shape
- low sperm count or slow motility (movement of sperm)
- high viscosity (sticky sperm sample)
- difficulty in ejaculation
- stenotic cervix (narrow cervical opening)
- donor sperm insemination
- unexplained infertility
- presence of anti-sperm antibodies against her partner
What studies should be done before recommending IUI?
1. Comprehensive Sperm Analysis
It is important to know the number of sperm available, what percentage of the sperm sample
are moving and the shape of the sperm cells.
IUI is most likely to be unsuccessful if
- the sperm count is under 10 million
- b. the sperm is slow moving or not moving at all (motility)
- the sperm morphology is under 4% normal morphology
2. Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
IUI is most likely to be successful if both fallopian tubes are healthy and open.
Hysterosalpingogram can clearly confirm this if the dye is able to flow easily through both tubes, so the ability of the tubes to pick up egg cell is greater.
If only one tube is open, IUI can still be done but we often recommend fertility medications so that both ovaries produce egg cells. Therefore, there will hopefully be egg cells available on both sides.
3. Adequate Egg Cell Quality
When the egg quality is good, there is a greater likelihood that the sperm can penetrate the egg and fertilize the egg. In addition, healthy eggs are more likely to continue to develop into a healthy embryo that will be successfully implanted into the lining of the uterus and result to pregnancy.
Tests that we perform to evaluate egg quality includes:
- Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH) – a fertility blood test that can be drawn any day of the menstrual cycle.
- Estradiol, LH, FSH, Progesterone – fertility blood tests that are most reliable when drawn during the first 5 days of the menstrual cycle.
- Antral Follicle Count – an ultrasound study that is most reliable when performed during the first 5 days of the menstrual cycle. The ovaries are observed and the number of follicles (which contain the egg cells) are counted in each ovary.
- Size of the ovaries – an ultrasound study that measures the dimensions of the ovary (length, width and height) and the overall volume of each ovary.
4. Vaginal Ultrasound and Pelvic MRI
Vaginal ultrasound and pelvic MRI are used to carefully observe both ovaries and the uterus. This is used to determine if there are no cysts in the ovaries and no large fibroids in the uterus, and no endometriosis or adenomyosis.
Natural Cycle vs. Fertility Medications
In the natural cycle, only one or two eggs will continue to develop, mature, and ovulate at the mid-cycle.
This means that only one or two eggs will be available to combine with sperm and achieve pregnancy.
Using fertility medications, several eggs will be available if the patient responds to the fertility medication.
The commonly used drugs to produce more egg cells includes:
- Clomiphene Citrate (Serophene®) and letrozole (Famara®) – These medications are taken orally for a period of five days and cause the release of FSH and LH, which stimulate the development of follicles. These medications are used in combination with injectable medications.
- Gonadotropins – These are injectable medications commonly prescribed to stimulate the ovaries of women. Three types of gonadotropins can be prescribed and are discussed below.
- FSH (Gonal-F®, Follistim®) – These medications contain only FSH and are administered on a daily basis by injection.
- LH (Low-dose hCG®) – This medication contains only LH and is administered by injection. It isused in combination with FSH containing medications.
- Human Menopausal Gonadotropins (Menopur®) – These medications contain equal amounts of FSH and LH, and are administered on a daily basis by injection.
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin [hCG] (Profasi®, Ovidrel®, Pregnyl®, Novarel®) – This medication contains the pregnancy hormone, hCG, which functions similarly to LH. It is administered approximately 36 hours before the eggs are retrieved.
- hCG is given by subcutaneous injection and matures the eggs, which will allow them to become fertilized.
Intrauterine Insemination: Step-by-step Process
STEP ONE: Determine if IUI is a good option for you
Vaginal ultrasound and pelvic MRI are used to carefully observe both ovaries and the uterus.
This is used to determine if there are no cysts in the ovaries and no large fibroids in the uterus, and no endometriosis or adenomyosis.
STEP TWO: Determine if fertility medications or natural cycle will be used for IUI
STEP THREE: Notify our office on the first day of your period
If you are using natural cycle, you will be given a schedule of which days to come in for monitoring.
If you are using medications, you will be given precise instructions at which date/s to start the medications.
For patients using Clomid or Letrozole, we generally start these medications on day 2 of the menstrual cycle. And you are seen in the office for office sonogram before starting the medication.
Your next visit will be two days after your last pill at which time you will have another blood test and sonogram.
If necessary, we may consider giving an injection of Gonal-F or Menopur to improve the egg quality.
STEP FOUR: Determine the day of insemination
We rely upon estradiol, LH, FSH, progesterone, as well as a vaginal sonogram to determine the best day for IUI. A follicle is considered as mature if it is greater than 20 millimeters in size.
The ovulation is usually based upon the drop in estradiol, the rise in LH, and the slight increase in progesterone.
Insemination is usually done on the day of the ovulation, as well as the next day.
STEP FIVE: Day of insemination
We generally do inseminations in the early afternoon and late evening between 5PM to 8PM.
The processing of sperm usually takes about 45 minutes.
Dr. Brandeis performs all inseminations personally.
Why is the Brandeis Fertility Center the best center to do Intrauterine Insemination in New York?
Dr. Brandeis personally does all inseminations.
- Over 30 years of experience with thousands of pregnancies achieved.
- Evening hours until 10PM, seven (7) days a week.
- The timing of insemination is critical for success. We determine the day of ovulation by:
- blood testing – rise of estradiol and LH (we do not use LH urine test)
- ultrasound is done to confirm if the follicles are ready and collapsed which is the best day to do insemination.
- Our cycle fee covers up to three inseminations.
- Insurance accepted for covered services.
- Patients are allowed to rest for 30 minutes after insemination.
- Patients are carefully monitored with blood work and ultrasound 2 weeks after the insemination.
- We encourage you to look at your sperm sample under the microscope both before and after sperm washing.
- If IUI is unsuccessful, we offer a free consultation to help you understand why the IUI did not work and discuss other treatment options.
- Prior to washing the sperm sample, we try to save some of the sperm to do a comprehensive sperm analysis at no extra charge.
- For patients using donor sperm, we can assist you in choosing your donor to consider by calling your chosen sperm bank with you to learn as much as possible about the sperm quality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is it necessary to wash the sperm sample to do IUI?
Yes. It is not advisable to inject the sperm sample in its natural form directly into the uterus.
This can cause extreme cramping and infection.
The sperm sample must be carefully processed to be able to separate the sperm cells from the sperm fluid to remove the seminal fluid which contains prostaglandins, infectious agents, and antigenic proteins.
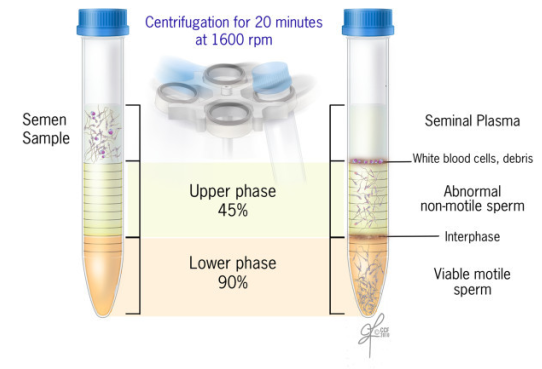

How do I know that it is my sperm sample?
All precautions are taken at every step to be sure that there is no chance for a “mix up”.
- Only one sperm sample is allowed in the laboratory at any time.
- After the sperm has been processed and used for insemination, the sperm container and all theplasticware used to prepare the sperm sample is discarded and removed from the laboratory.
What is the success rate for IUI?
In general, the success rate for intrauterine insemination in the medical literature is reported to be between
5-15% per cycle.
However, there are many factors that affect the likelihood of success.
These include:
- Ages of the couple
- History of repeated miscarriage, endometriosis, adenomyosis, pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Whether or not fertility medications were used.
- True quality of the egg and sperm
- Factors in the uterus itself such as fibroids or scarring in the cavity, whether or not the tubes are open.
- Medical conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, smoking or vaping – all of which have an impact.
Many studies indicate that 90-95% of pregnancies that do occur in IUI will happen during the first 3-4 months. It should be remembered that IUI is only a shortcut, allowing the sperm to get close to the egg by going to the top of the uterus.
After that, the sperm must be able to “swim up” into the fallopian tube, reach the egg in the tube, and fertilize it, and then the embryo must travel back into the uterus, then implant itself to the uterus and continue to develop.
The age of the patient is the most important factor because of the fact of egg quality. In patients who are over 40, the likelihood of success is therefore quite low with IUI.
The likelihood of success is generally presented as follows:
| Age | Percentage of Success (per cycle) |
| Under 35 | 15 to 20% |
| 35 – 40 | 10% |
| 40 or more | 5% |
Patients who have irregular cycles do not ovulate on a regular, predictable basis. These patients often have PCOS which is present in 1 in 10 women.
These patients often require medication such as Clomid or Letrozole.
When Clomid or Letrozole is unsuccessful to causing a regular ovulation, it is necessary to add fertility injections such as Gonal-f or to use only Gonal-f and Menopur, and not use oral medication.
The success rate of IUI will improve when fertility medications are added because there are more eggs available.
Male factor infertility is found in almost 40% of infertility couples. IUI can be a benefit by concentrating all healthy sperm into one or two drops. However, one must be aware that IUI facilitates by acting as a shortcut to get more sperm higher up near the fallopian tube. But if the sperm count is very low or there is a low number of normal-shaped sperm, IVF may be a better option.
It is commonly accepted by many fertility specialists that after the sperm has been processed, there should be at least 10 million moving sperm in the post-washed sample to have a realistic chance of success.
Unexplained infertility is found for 10-25% of infertile couples. The generally accepted definition of unexplained infertility is that no factor for fertility can be identified after doing the conventional test – the x-ray of the tubes is normal, AMH is over 1.5, antral follicle count is over seven (7), the sperm analysis is adequate.
According to many reports in literature, in patients with unexplained infertility, the likelihood of success for IUI is 7-10% per cycle without medication.
In patients with 3 IUI cycle using Clomid or Letrozole, the success rate can range from 15-25%.
Success with IUI when only one tube is open
The likelihood of pregnancy is very much related to where the blockage of tubes is.
If the blockage is at the top of uterus, there is a higher success rate than when the blockage is at the bottom of the tube.
How much does IUI cost?
Intrauterine Insemination (without monitoring) $300
- Sperm preparation of fresh partner or frozen donor sperm
- Vaginal ultrasound
- Insemination by Dr. Brandeis personally
Complete IUI Cyle (Monitoring and Insemination) $800
- Sperm preparation of fresh partner or frozen donor sperm
- Monitoring – up to 4 vaginal ultrasounds and office visits
- 1-3 inseminations per cycle


